What is Ozone?
1562283 Views
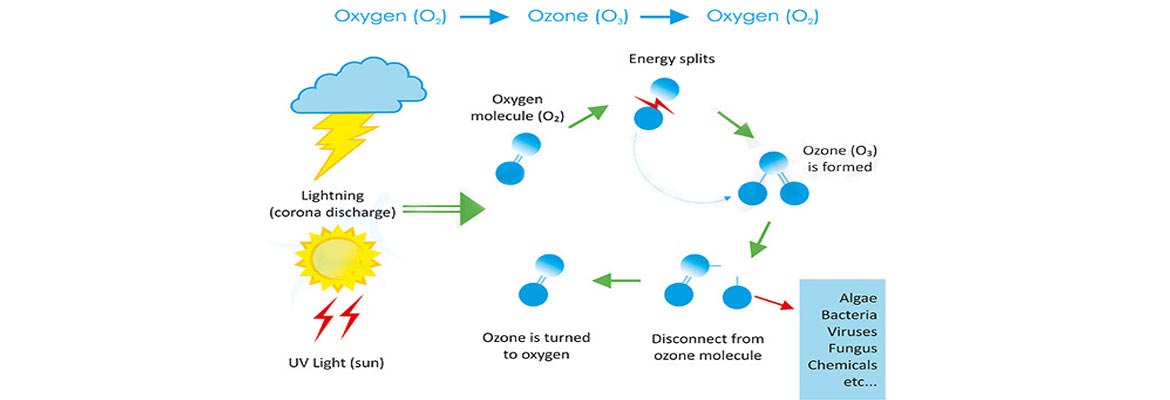
Ozone is a gas that most people commonly associate with the thin layer above the Earth's atmosphere that protects us from the sun's ultraviolet rays. However, this blue gas, sometimes described as having a "fresh smell" after lightning, has various applications on Earth.
Ozone is composed solely of oxygen. It can be visualized as a regular O2 molecule with a highly reactive, energetic, and unstable single O1 atom. This O1 atom does not prefer to exist alone and tends to stabilize by bonding with another O2 molecule, forming ozone (O3). Ozone is injected into water or air, where the additional oxygen provides high capabilities for destroying cell walls, microorganisms, and oxidizing metals in water. High-frequency ozone production has several benefits, including reducing the size of ozone generators and producing high-capacity, high-concentration ozone. Advanced design in voltage systems and ozone reactors at Rashkian ensures that ozone reactors operate at higher temperatures, and air-cooled models can achieve very high capacities.
How Does Ozone Work?
Ozone is a strong disinfectant and oxidizer, affecting any pathogen or contaminant through oxidation, disinfection, alteration, or removal. It is the strongest disinfectant available for water treatment, second only to fluorine in oxidizing power. Compared to chlorine, the most common water disinfectant, ozone is over 50% more powerful as an oxidizer and acts over 3000 times faster. Both chlorine and fluorine are highly toxic chemicals.
For over a century, ozone has been used to purify drinking water in Europe. In the United States, ozone is used for bottling water and cooling tower disinfection. Los Angeles, for instance, currently uses ozone for its water supply. Ozone’s applications are not limited to drinking water.
On June 23, 2001, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) officially granted ozone GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) status for use in food contact applications. With FDA approval, food processors quickly adopted this exciting new technology in their plants.
Today, ozone technology is used in processing meat, poultry, seafood, and fresh produce as a safe method for managing food safety. Food processors recognize that ozone extends the shelf life of their products, a crucial advantage in today’s competitive global food industry.
History of Ozone:
- 1840 - Discovered by Schnebein
- 1893 - Used as a disinfectant in drinking water
- 1909 - Used as a food preservative for frozen meat
- 1939 - Found to prevent yeast and mold growth during fruit storage
- 1982 - FDA GRAS declaration for bottled water
- 1995 - FDA GRAS status for fresh bottled water remains unchanged
- 1997 - Industry experts confirm ozone GRAS and compliance with FDA requirements
- 1999 - USDA rejects ozone protocol for meat, citing 1982 GRAS declaration for water
- 2000 - Petition for Food Additive, including ozone use in water and air, is under preparation. FDA estimates approval within six months after submission.

 عربی
عربی
 فارسی
فارسی